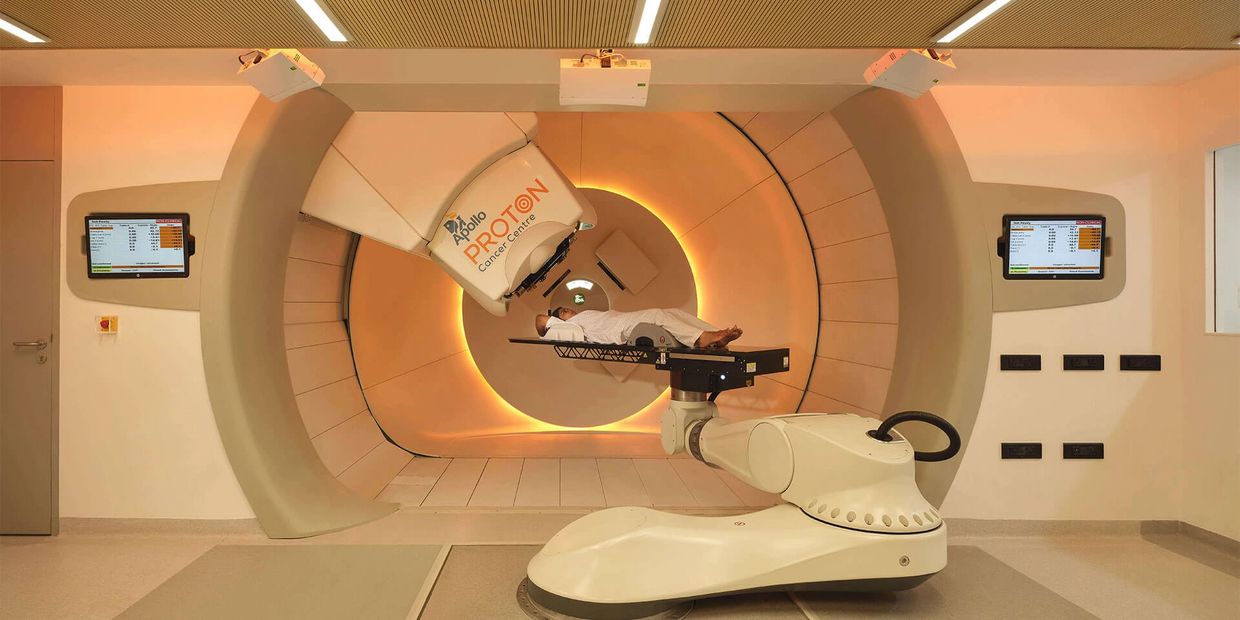
Proton Therapy under Dr. Vineet Nakra
Proton Beam Therapy
Proton beam therapy is a type of radiation therapy that uses high-energy protons to treat cancer and some noncancerous tumors. Protons are positively charged particles that are separated from hydrogen atoms and sped up in a particle accelerator such as a synchrotron or cyclotron. Proton beam therapy works by disrupting the tumor's DNA and destroying tumor cells. Protons have unique properties that allow doctors to better target radiation to the size and shape of the tumor, while sparing more of the surrounding healthy tissue.
What are the uses and advantages of proton beam therapy?
Proton beam therapy can be used to treat tumors composed of different types of cells and located in different parts of the body, such as brain, spinal cord, head and neck, breast, lung, liver, pancreas, rectum, prostate, eye and sarcomas. Proton beam therapy can also be used to treat tumors that come back and need repeat courses of radiation (reirradiation).
Some of the advantages of proton beam therapy are:
- It can deliver a higher dose of radiation to the tumor than conventional X-ray radiation, which may increase the chance of curing or controlling the cancer.
- It can reduce the exposure of normal tissues and organs to radiation, which may lower the risk of side effects and long-term complications such as secondary cancers.
- It can be more precise and conformal than other forms of radiation therapy, which may allow for better preservation of function and quality of life.
- It can be more suitable for treating tumors near critical structures such as the brainstem, spinal cord, optic nerves and heart.
- It can be more effective for treating tumors that are resistant to conventional radiation therapy due to their location or biology.
What are the limitations and challenges of proton beam therapy?
Proton beam therapy is not widely available and accessible due to its high cost and complexity. There are only a few proton therapy centers in the world, and they require specialized equipment and staff. Proton beam therapy is also not covered by all insurance plans, which may limit its affordability for some patients.
Proton beam therapy is not suitable for all types of tumors and patients. Some tumors may be better treated with other forms of radiation therapy or other modalities such as surgery or chemotherapy. Proton beam therapy may also have some side effects and risks, such as skin reactions, fatigue, nausea, hair loss, inflammation and infection. Proton beam therapy may also cause damage to healthy tissues that are in the path of the proton beam or near the exit point of the protons.
Proton beam therapy is still an evolving field that requires more research and evidence to establish its safety, efficacy and cost-effectiveness compared with other treatments. There are still many uncertainties and controversies regarding the optimal dose, technique and indications for proton beam therapy¹². More clinical trials and studies are needed to compare proton beam therapy with other forms of radiation therapy and to evaluate its long-term outcomes and benefits.
Proton beam therapy is a promising form of radiation therapy that uses high-energy protons to treat cancer and some noncancerous tumors. It has several advantages over conventional X-ray radiation, such as higher precision, lower toxicity and better preservation of function. However, it also has some limitations and challenges, such as high cost, limited availability and lack of conclusive evidence. Proton beam therapy is not a panacea for all types of tumors and patients, but it may offer a better option for some cases that are difficult or impossible to treat with other modalities.
Proton Therapy in Delhi-NCR
There is currently no hospital in Delhi-NCR with the infrastructure for proton beam therapy. However, Dr. Vineet Nakra is an expert in proton beam therapy and has an extensive experience from his association with Apollo Proton Cancer Centre in Chennai. To book an appointment with Dr. Vineet Nakra to discuss if you may benefit from proton therapy, click below.
Copyright © 2020-2025 Dr. Vineet Nakra - All Rights Reserved.
.png/:/rs=h:146,cg:true,m/qt=q:95)